Heat Stress in the Workplace : A Smart, Comprehensive Guide to Protecting Your Crew
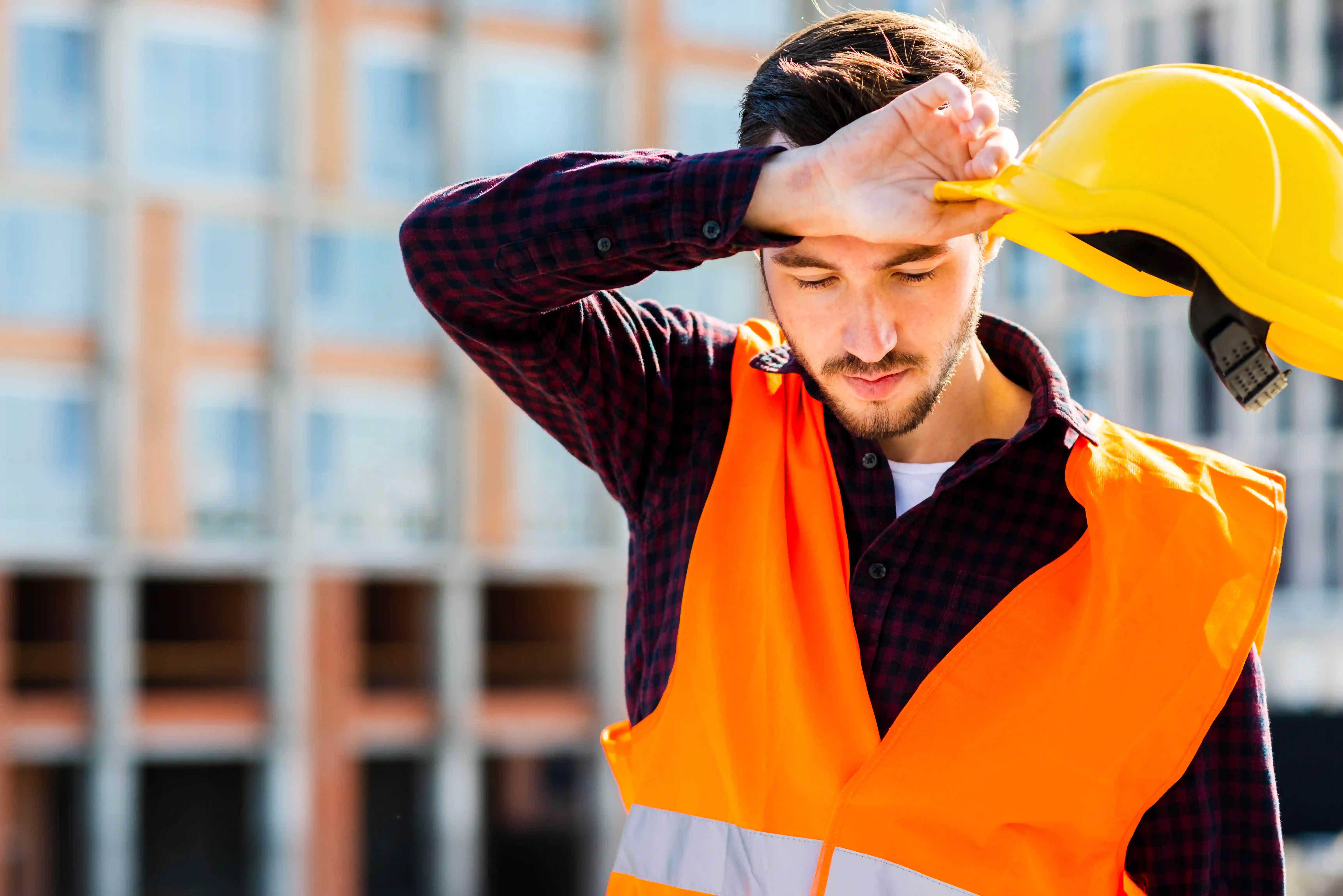

As summer turns up the heat each year, workplace heat stress becomes not just a discomfort, but a serious hazard. Across industries—from Arizona construction sites to Midwest warehouses—the combination of rising temperatures, intense labor, and protective gear is fueling a surge in heat-related illnesses. The good news? With proactive strategies, smart equipment, and a commitment to safety, heat stress is preventable. Here's your go-to guide for building a healthier, more productive workforce..
1. What Is Heat Stress — and Why It Matters
Heat stress occurs when the body can't shed enough heat. This can result from:
- High ambient temperature or humidity
- Direct sun exposure
- Intense physical labor
- Heavy PPE that blocks sweat evaporation
Early signs include heat rash and cramps, but if neglected, it can lead to heat exhaustion and fatal heat stroke. Plus, as temperatures climb, productivity plummets—studies show a 1–2% output drop for every degree above 77°F. In short: heat kills, and it costs.
2. Who's Most at Risk?
Outdoor workers
Construction, agriculture, landscaping
Indoor staff
Manufacturing, bakeries, warehouses, boiler rooms
New hires or returning workers
Not yet acclimatized to heat
People wearing heavy PPE
Or with health conditions that impair cooling
Workers over 60
pregnant individuals, or those with underlying health
issues
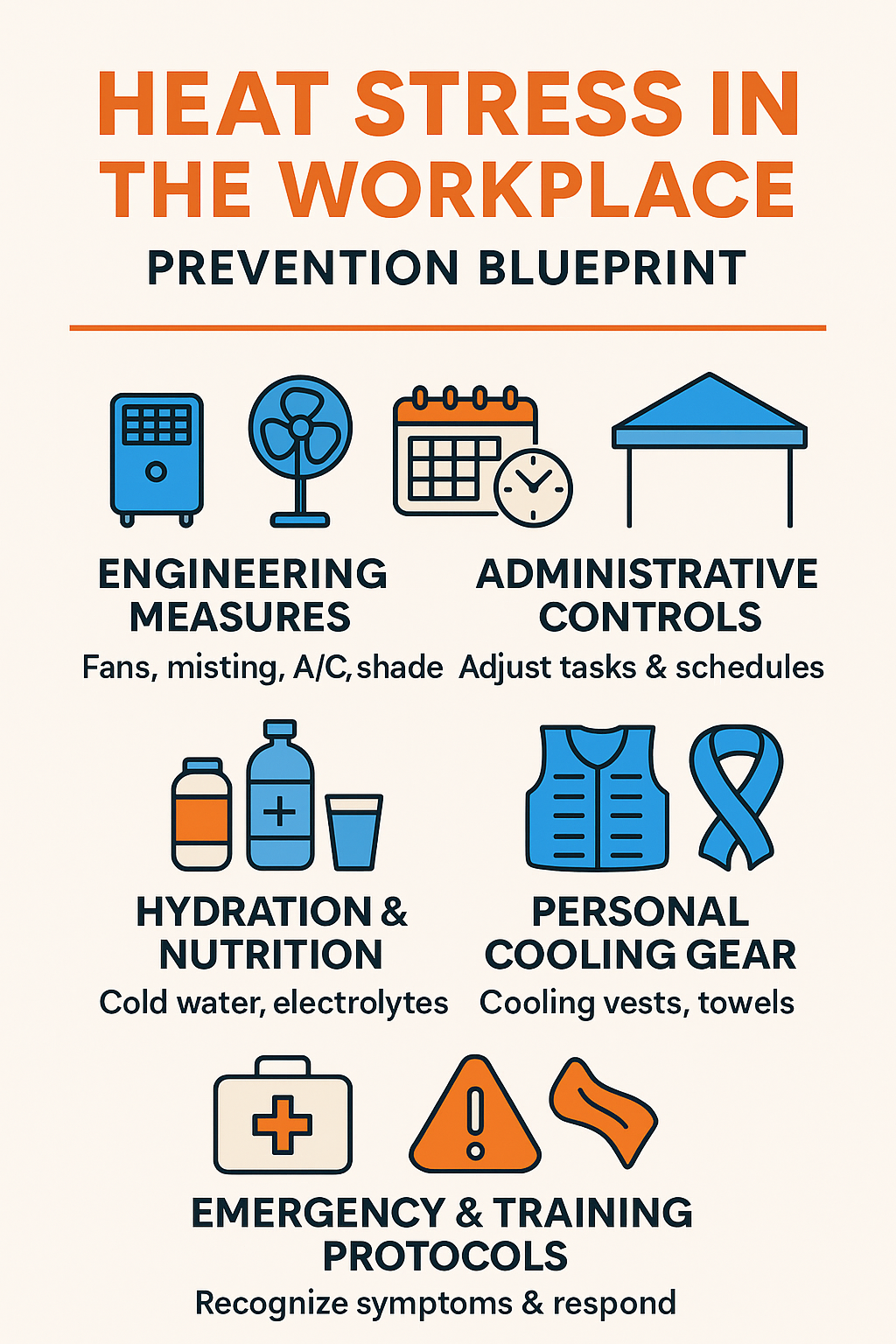
3. The Five-Step Prevention Blueprint
1. Engineering Measures
- Install fans, misting systems, or air-conditioning
- Use reflective shade canopies and portable cooling tents
- Insulate hot surfaces and ventilate enclosed spaces
2. Administrative Controls
- Schedule strenuous tasks during cooler parts of the day
- Enforce the essential rule: Water. Rest. Shade.
- Implement acclimatization programs: gradually ramping exposure over 7–14 days.
3. Hydration & Nutrition
- Provide cold water, hydration packs, jug coolers
- Offer electrolyte drinks to replenish lost salts
- Encourage drinking before thirst hits—up to 8–11 liters daily on hot days
4. Personal Cooling Gear
- Use cooling vests, neck towels, UV-protective clothing, and cooling PPE
- Shield skin with sunscreen, hats, and breathable fabrics
5. Emergency & Training Protocols
- Educate everyone on recognizing and responding to heat illness
- Encourage buddy systems so coworkers can monitor each other
- Keep cooling resources (packs, fans, cold water) handy onsite
- Create clear first aid procedures: for heat exhaustion—move to shade, hydrate, cool; for heat stroke—this is an emergency—call medical help immediately
4. Optimize the Workspace with the Right Equipment
These solutions go beyond comfort—they reduce absences, preserve productivity, and support overall worker morale.
5. Arizona’s Leading Role in Heat Safety
In states like Arizona—where temperatures often exceed 100 °F—heat safety isn’t optional. The Arizona Division of Occupational Safety and Health (ADOSH) leads with:
- ✅ On-site inspections and free consultations
- ✅ Heat Safety Task Force delivering statewide guidelines
- ✅ Multilingual resources and official recognition for compliant employers
These efforts aren’t just regulatory—they reflect a commitment to progress and worker wellbeing.

6. Cultivating a Safe-First Culture
Real progress comes from embedding safety into your values:
- Leadership shows care by enforcing policies and walking the talk
- Workers remind each other to hydrate, rest, and watch for symptoms
- Regular communication and visible signage in multiple languages reinforce awareness
- Tools like mobile heat-index apps or WBGT meters enable data-backed decisions
7. Beyond Prevention: Sustainability Matters
Global industrial efforts also spotlight the importance of green practices:
- 🌱 Use solar or wind energy to power cooling systems
- 🌱 Choose energy-efficient fans and chillers
- 🌱 Partner with eco-conscious suppliers
By preventing heat illness and reducing your carbon footprint, you protect both your team and the planet.

Final Takeaways
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Assess risk factors: heat, humidity, workload, health status |
| 2 | Control exposure using engineering, admin, and PPE practices |
| 3 | Train everyone—recognize symptoms and know how to respond |
| 4 | Equip work areas with adequate cooling gear and hydration access |
| 5 | Engage culture—support each other with a safety-first mindset |
Ready to Protect Your Team?
Implementing these strategies saves lives, reduces legal liability, and boosts performance—because safe workers are engaged workers.
Spread the Word
Feel empowered? Share this guide with your team, across industries, and in your community. Let’s all embrace smarter, safer summer work—because every shift should end with everyone going home well

Recommended Heat Stress Prevention Products
Sources to buy the products you need :
